| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||||
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 |
- 사전예약
- MOBI
- 모바일게임
- 용의후예
- 사코
- 원스토어
- 사전쿠폰
- 캐시슬라이드
- 게임코드
- 모바일쿠폰
- 쿠폰
- 칼이쓰마
- 겜셔틀
- 제존:혼돈의 시대
- 아리아 레전드
- 보너스
- 코드뱅크
- 게임쿠폰
- 모비
- 테이아
- 넥슨
- 검과마법 for Kakao
- 사전코드
- 미인강호
- 사전에약
- 판타지스쿼드
- 삼국크러쉬
- CODEBANK
- 보너스쿠폰
- 예약TOP10
- Today
- Total
자료수집소
포트 미러링 이란? 본문
포트 미러링
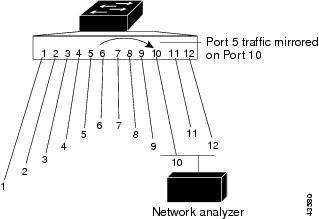
포트 미러링(Port Mirroring)은 네트워크 스위치의 어떤 한 포트에서 보이는 모든 네트워크 패킷 혹은 전체 VLAN의 모든 패킷들을 다른 모니터링 포트로 복제하는데 사용된다. 포트 미러링은 주로 침입 탐지 시스템이나 패시브 프로브 또는 애플리케이션 성능 관리(Application Performance Management, APM)에 필요한 실사용자 모니터링(Real User Monitoring, RUM) 기술과 같이 네트워크 트래픽을 모니터링 해야하는 네트워크 장비들에서 사용된다. 포트미러링은 시스코 스위치에선 일반적으로 스위치 포트 분석기(Switched Port ANalyzer, SPAN) 혹은 원격 스위치 포트 분석기(Remote Switched Port ANalyzer, RSPAN)라 불린다. 다른 제조사들에서는 다른 이름으로 부르곤 하는데, 3Com의 경우 로빙 분석 포트(Roving Analysis Port, RAP)라 부른다.
네트워크 엔지니어/관리자는 포트 미러링을 네트워크상의 데이터를 분석 및 디버그하거나 오류를 진단하는데 사용한다. 포트 미러링은 또한 관리자가 네트워크 성능을 관찰하는데 도움을 주고, 문제가 발생했을 때 이를 알려준다. 또한 인바운드나 아웃바운드 트래픽 중 하나 혹은 전부를 하나 또는 여러개의 인터페이스로 미러링하는데 사용할 수 있다.
1. CISCO 포트 미러링(SPAN) 명령어
- 포트 gi0/5번 in, out 패킷을 gi0/10번으로 미러링
Switch#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)#monitor session 1 source interface GigabitEthernet 0/5
Switch(config)#monitor session 1 destination interface GigabitEthernet 0/10
- 포트 gi0/5번 in 패킷을 gi0/10번으로 미러링
Switch#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)#monitor session 1 source interface GigabitEthernet 0/5 rx
Switch(config)#monitor session 1 destination interface GigabitEthernet 0/10
- 포트 gi0/5번 out 패킷을 gi0/10번으로 미러링
Switch#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)#monitor session 1 source interface GigabitEthernet 0/5 tx
Switch(config)#monitor session 1 destination interface GigabitEthernet 0/10
[출처] 시스코스위칭에서의 포트미러링 방법|작성자 보물섬
참고자료 : CISCO 가이드----------------------------------
Creating a Local SPAN Session
Follow these steps to create a SPAN session and specify the source (monitored) ports or VLANs and the destination (monitoring) ports.
1. enable
3. no monitor session {session_number | all | local | remote}
4. monitor session session_number source {interface interface-id | vlan vlan-id} [, | -] [both | rx | tx]
5. monitor session session_number destination {interface interface-id [, | -] [encapsulation replicate]}
8. copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
Creating a Local SPAN Session and Configuring Incoming Traffic
Follow these steps to create a SPAN session, to specify the source ports or VLANs and the destination ports, and to enable incoming traffic on the destination port for a network security device (such as a Cisco IDS Sensor Appliance).
1. enable
3. no monitor session {session_number | all | local | remote}
4. monitor session session_number source {interface interface-id | vlan vlan-id} [, | -] [both | rx | tx]
5. monitor session session_number destination {interface interface-id [, | -] [encapsulation replicate] [ingress {dot1q vlan vlan-id | untagged vlan vlan-id | vlan vlan-id}]}
8. copy running-config startup-config
DETAILED STEPS
| Command or Action | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1 | enable Example: Switch> enable
| Enables privileged EXEC mode. Enter your password if prompted.
|
| Step 2 | configure terminal Example: Switch# configure terminal | |
| Step 3 | no monitor session {session_number | all | local | remote} Example: Switch(config)# no monitor session all | |
| Step 4 | monitor session session_number source {interface interface-id | vlan vlan-id} [, | -] [both | rx | tx] Example: Switch(config)# monitor session 2 source gigabitethernet1/0/1 rx | Specifies the SPAN session and the source port (monitored port). |
| Step 5 | monitor session session_number destination {interface interface-id [, | -] [encapsulation replicate] [ingress {dot1q vlan vlan-id | untagged vlan vlan-id | vlan vlan-id}]} Example: Switch(config)# monitor session 2 destination interface gigabitethernet1/0/2 encapsulation replicate ingress dot1q vlan 6 | Specifies the SPAN session, the destination port, the packet encapsulation, and the ingress VLAN and encapsulation.
|
| Step 6 | end Example: Switch(config)# end | |
| Step 7 | show running-config Example: Switch# show running-config | |
| Step 8 | copy running-config startup-config Example: Switch# copy running-config startup-config
| (Optional) Saves your entries in the configuration file. |
'< 컴퓨터 > > 네트워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알카텔 6850] CRC에러 카운터 초기화 (0) | 2016.09.09 |
|---|---|
| [알카텔 6850] Config 저장 안되는 현상 (0) | 2016.09.09 |
| three-Way Handshaking 이란? (0) | 2016.05.03 |